구조화 된 구조화 + 구조화되지 않은 데이터가 AI를 사용한 우편둥이에서 흐릅니다.
cocoindex 점진적인 데이터 흐름을 구축하기위한 하나의 프레임 워크입니다 구조화되고 구조화되지 않았습니다 출처.
Cocoindex에서 AI 단계는 임베드 생성과 같은 다른 유형의 변환과 동일한 흐름, 예를 들어 데이터 매핑, 계산 등과 동일한 흐름으로 변환됩니다.
구조화되지 않은 + 비 구조화에 대한 하나의 프레임 워크는 무엇입니까?
- 하나의 정신 모델 : 파일, API 및 데이터베이스를 균일하게 처리합니다. AI 단계는 일반적인 작전입니다.
- 기본적으로 증분 : 서수를 사용하여 변경 만 동기화합니다. 깨지기 쉬운 접착제 작업이 없습니다.
- 일관성 : 임베딩은 항상 정확한 변환 된 행 상태에서 파생됩니다.
- 운영 단순성 : 하나의 배포, 1 개의 계보보기, 이동 부품이 적습니다.
이 블로그는 새로운 PostgreSQL 소스를 소개하고 PostgreSQL 테이블에서 소스로 데이터를 가져오고 AI 모델 및 비 AI 계산으로 변환하는 방법을 보여주고 Semantic + Structured 검색을 위해 새로운 PostgreSQL 테이블에 작성합니다.
이것이 당신을 도울 경우, Star Cocoindex github!
예 : PostgreSQL 제품 인덱싱 흐름
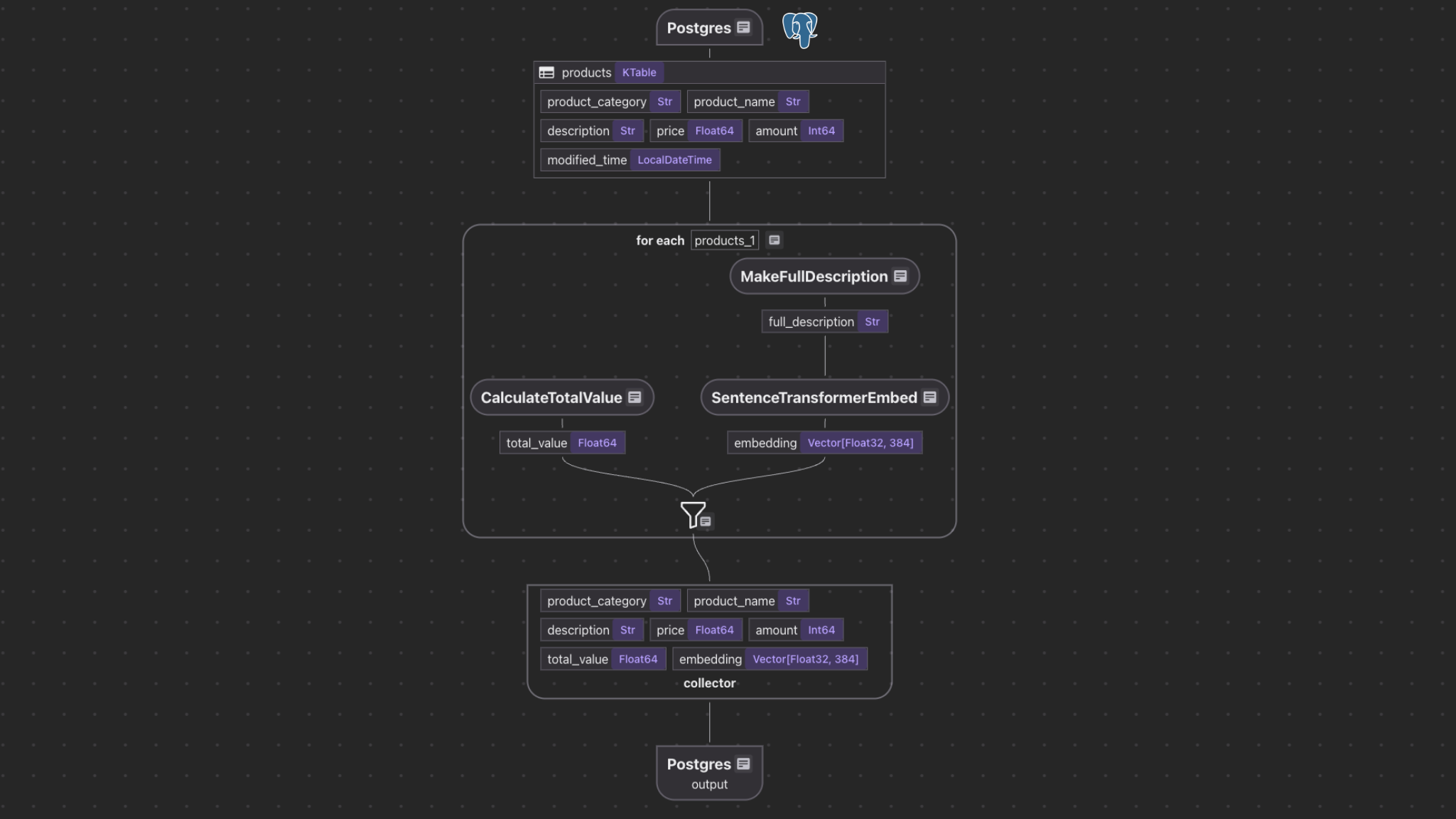
우리의 예는 보여줍니다
- PostgreSQL 테이블의 데이터를 읽습니다
source_products. - 추가 필드 컴퓨팅 (
total_value,,,full_description). - 시맨틱 검색을위한 임베딩 생성.
- 벡터 인덱스를 사용하여 결과를 다른 PostgreSQL 테이블에 저장 pgvector
이 예제는 오픈 소스 – 예/postgres_source입니다.
소스에 연결하십시오
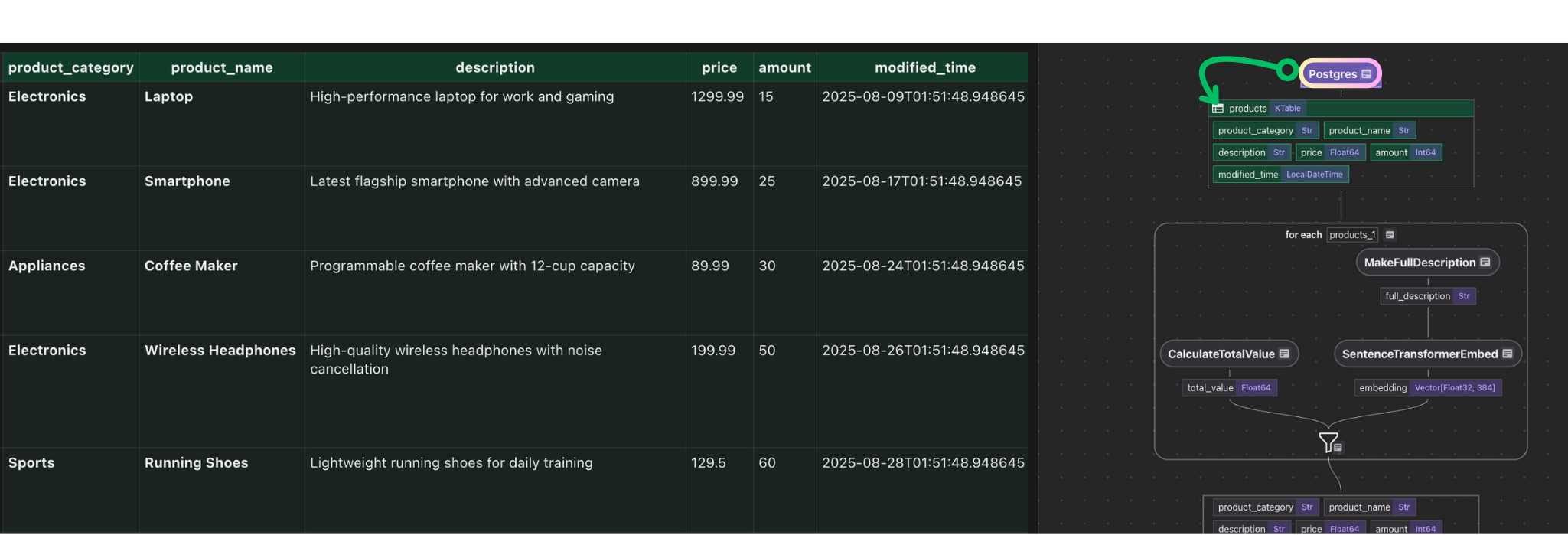
flow_builder.add_source 행을 읽습니다 source_products.
@cocoindex.flow_def(name="PostgresProductIndexing")
def postgres_product_indexing_flow(flow_builder: cocoindex.FlowBuilder, data_scope: cocoindex.DataScope) -> None:
data_scope["products"] = flow_builder.add_source(
cocoindex.sources.Postgres(
table_name="source_products",
# Optional. Use the default CocoIndex database if not specified.
database=cocoindex.add_transient_auth_entry(
cocoindex.DatabaseConnectionSpec(
url=os.environ["SOURCE_DATABASE_URL"],
)
),
# Optional.
ordinal_column="modified_time",
notification=cocoindex.sources.PostgresNotification(),
),
)
이 단계는 PostgreSQL 테이블의 소스 데이터를 추가합니다 source_products 흐름에 a KTable.
\
- 증분 동기화 : 새 또는 업데이트 된 행이 발견되면 해당 행만 파이프 라인을 통해 실행되므로 다운 스트림 인덱스와 검색 결과는 최신 데이터를 반영하고 변경되지 않은 행은 손대지 않았습니다.
ordinal_column변경 감지에 권장되어 파이프 라인이 변경된 내용을 처리합니다.notification: 존재하면 Postgres Listen/Notify를 기반으로 변경 캡처를 활성화하십시오.
자세한 내용은 Postgres 소스를 확인하십시오.
Supabase가 호스팅 한 Postgres 데이터베이스를 사용하는 경우 프로젝트 대시 보드에서 연결을 클릭하고 URL을 찾으십시오. 자세한 내용은 DatabaseConnectionspec을 확인하십시오.
간단한 데이터 매핑 / 변환
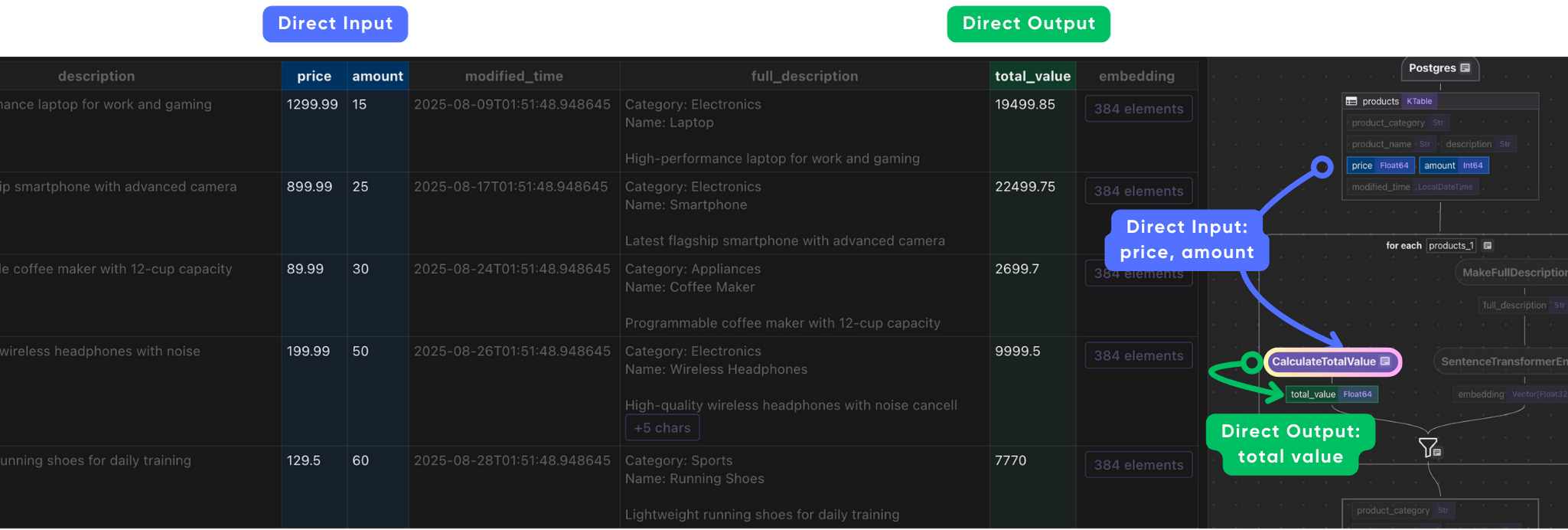
총 가격을 계산하기 위해 간단한 변환을 만듭니다.
@cocoindex.op.function()
def calculate_total_value(price: float, amount: int) -> float:
"""Compute total value for each product."""
return price * amount
흐름에 플러그 :
with data_scope["products"].row() as product:
# Compute total value
product["total_value"] = flow_builder.transform(
calculate_total_value,
product["price"],
product["amount"],
)
데이터 변환 및 AI 변환
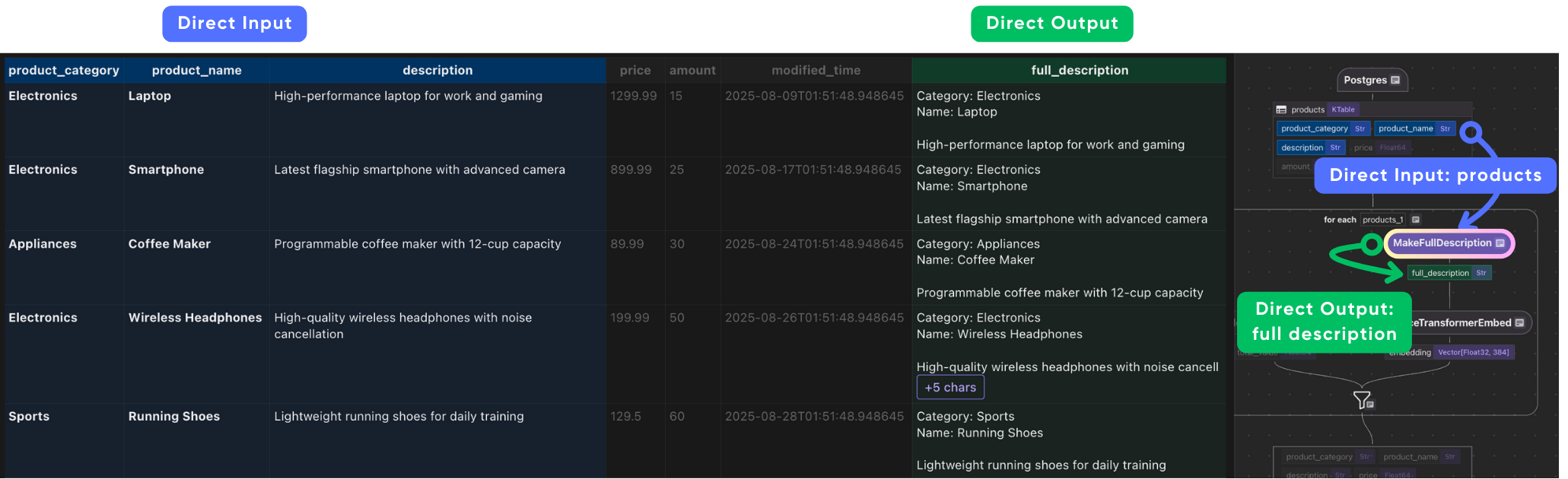
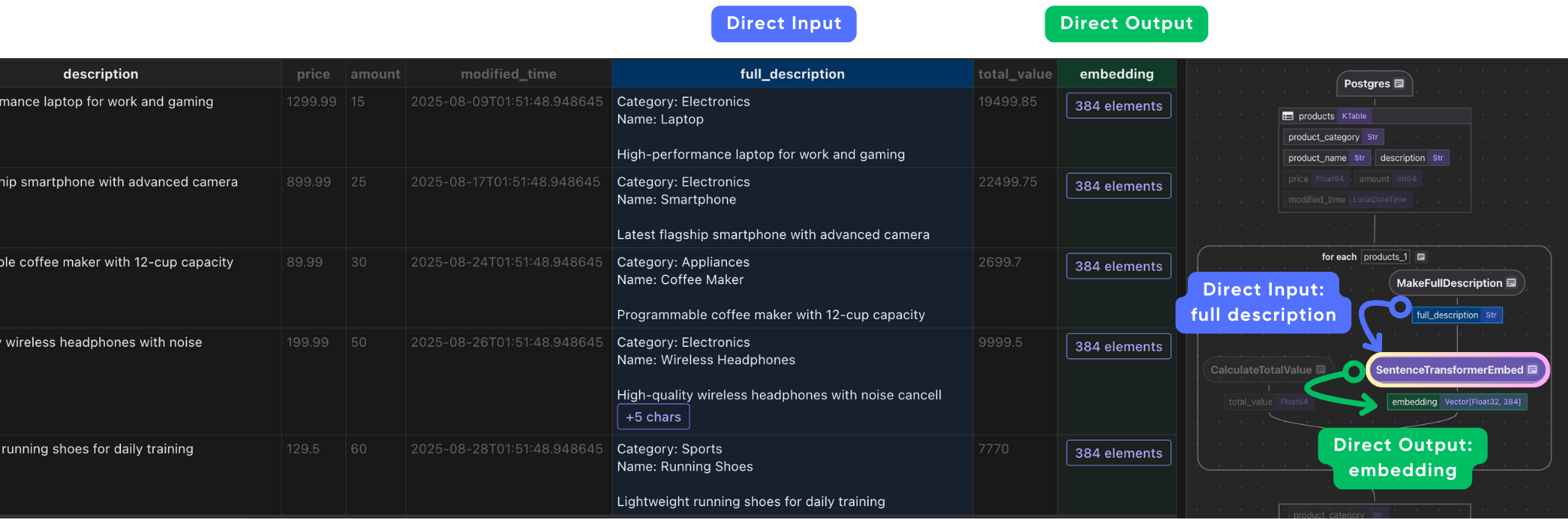
사용자 정의 함수 생성 a full_description 제품의 범주, 이름 및 설명을 결합하여 필드.
@cocoindex.op.function()
def make_full_description(category: str, name: str, description: str) -> str:
"""Create a detailed product description for embedding."
return f"Category: {category}\nName: {name}\n\n{description}"
임베딩은 종종 더 많은 맥락에서 더 잘 수행됩니다. 필드를 단일 텍스트 문자열로 결합함으로써 제품의 의미 론적 의미가 완전히 캡처되도록합니다.
이제 흐름에 연결하십시오.
with data_scope["products"].row() as product:
#.. other transformations
# Compute full description
product["full_description"] = flow_builder.transform(
make_full_description,
product["product_category"],
product["product_name"],
product["description"],
)
# Generate embeddings
product["embedding"] = product["full_description"].transform(
cocoindex.functions.SentenceTransformerEmbed(
model="sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"
)
)
# Collect data
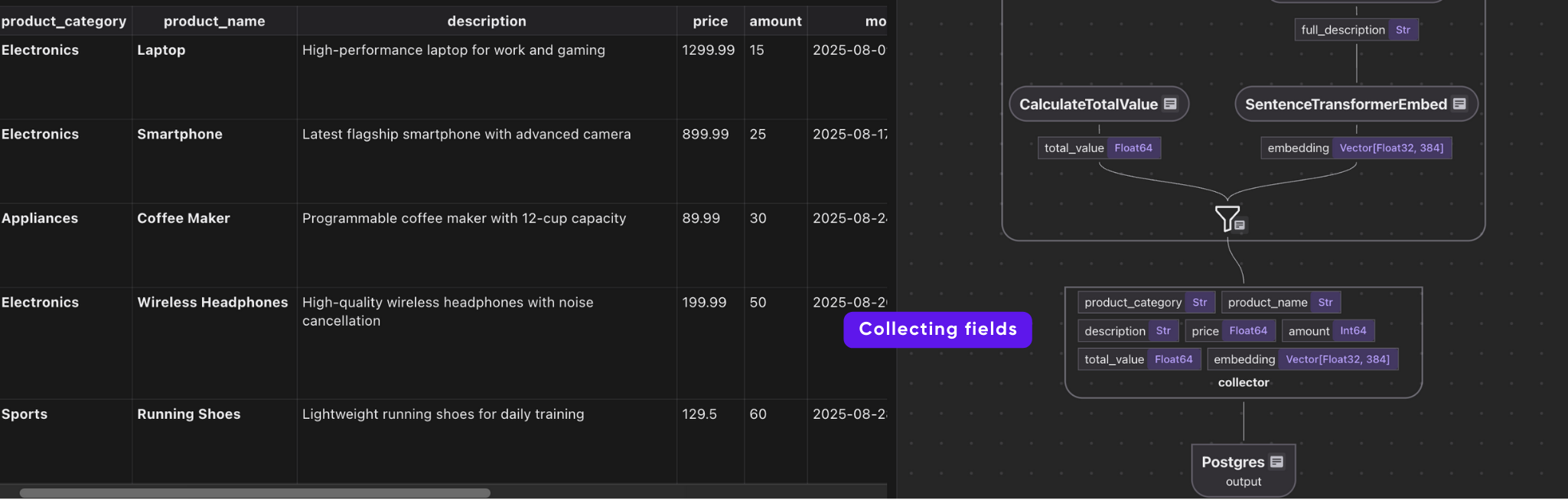
indexed_product.collect(
product_category=product["product_category"],
product_name=product["product_name"],
description=product["description"],
price=product["price"],
amount=product["amount"],
total_value=product["total_value"],
embedding=product["embedding"],
)
이것은 각 제품 행을 취하고 다음을 수행합니다.
-
풍부한 설명을 구축합니다.
\
-
그것을 삽입으로 바꿉니다
\
-
구조화 된 필드 (카테고리, 이름, 가격 등)와 함께 임베딩을 수집합니다.
내보내다
indexed_product.export(
"output",
cocoindex.targets.Postgres(),
primary_key_fields=["product_category", "product_name"],
vector_indexes=[
cocoindex.VectorIndexDef(
field_name="embedding",
metric=cocoindex.VectorSimilarityMetric.COSINE_SIMILARITY,
)
],
)
모든 변환 된 행은 수집 및 벡터 인덱스가있는 새로운 PostgreSQL 테이블로 내보내며 시맨틱 검색이 준비됩니다.
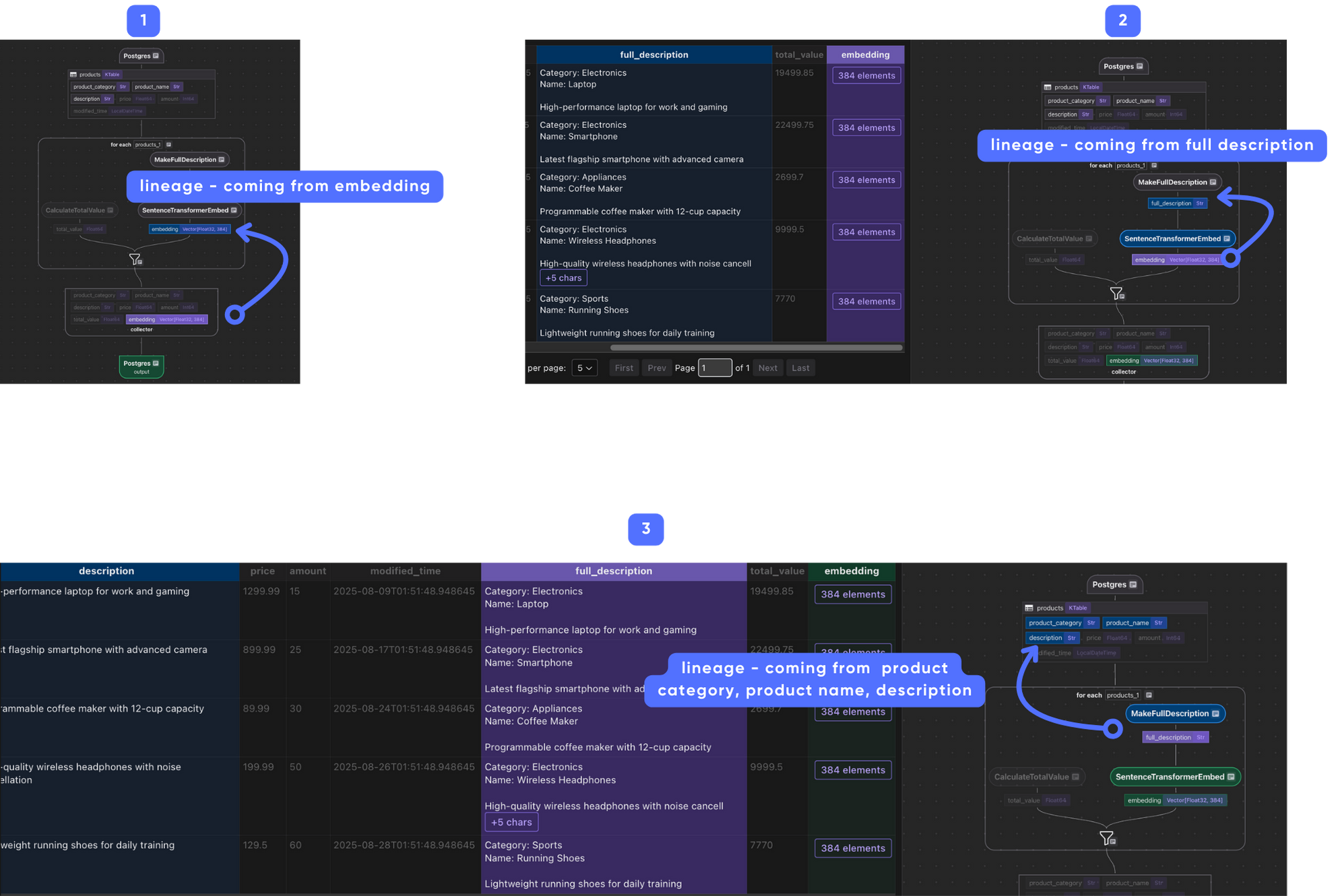
현장 계보
변환 흐름이 복잡해지기 시작하면 각 필드가 어떻게 도출되는지 이해하기가 어렵습니다. CocoIndex는 각 필드의 계보를 시각화하여 필드 원산지 및 다운 스트림 종속성을보다 쉽게 추적하고 문제를 해결할 수 있도록합니다.
예를 들어, 다음 이미지는 embedding 필드, 최종 출력에서 후방에서 소스 필드로, 단계별로 클릭 할 수 있습니다.
파이프 라인 실행
- 종속성 설정 :
pip install -e .
- 샘플 데이터로 소스 테이블 작성 :
psql "postgres://cocoindex:cocoindex@localhost/cocoindex" -f ./prepare_source_data.sql
- 테이블 설정 및 인덱스 업데이트 :
cocoindex update --setup main.py
- Cocoinsight 실행 :
cocoindex server -ci main
Cocoinsight에서 프로젝트를 단계별로 걸어 가면 각 필드가 어떻게 구성되는지와 무대 뒤에서 발생하는 일을 정확히 알 수 있습니다. 파이프 라인 데이터 보유가없는 로컬 CocoIndex 서버에 연결됩니다.
지속적인 업데이트
소스가 변경되면 지속적인 업데이트를 위해 추가하십시오 -L:
cocoindex server -ci -L main
자세한 내용은 라이브 업데이트를 확인하십시오.
인덱스를 검색하고 쿼리하십시오
질문
인덱스 된 제품 테이블을 통해 시맨틱 유사성 검색을 실행하여 주어진 쿼리의 최고 일치를 반환합니다.
def search(pool: ConnectionPool, query: str, top_k: int = 5) -> list[dict[str, Any]]:
# Get the table name, for the export target in the text_embedding_flow above.
table_name = cocoindex.utils.get_target_default_name(
postgres_product_indexing_flow, "output"
)
# Evaluate the transform flow defined above with the input query, to get the embedding.
query_vector = text_to_embedding.eval(query)
# Run the query and get the results.
with pool.connection() as conn:
register_vector(conn)
with conn.cursor(row_factory=dict_row) as cur:
cur.execute(
f"""
SELECT
product_category,
product_name,
description,
amount,
total_value,
(embedding <=> %s) AS distance
FROM {table_name}
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT %s
""",
(query_vector, top_k),
)
return cur.fetchall()
이 기능
- 쿼리 텍스트를 임베딩으로 변환합니다 (
query_vector). - 각 제품의 저장된 임베딩과 비교합니다 (
embedding) 벡터 거리 사용. - 메타 데이터와 유사성 점수를 포함하여 가장 가까운 경기를 반환합니다 (
distance).
명령 줄 대화식 루프를 만듭니다
def _main() -> None:
# Initialize the database connection pool.
pool = ConnectionPool(os.environ["COCOINDEX_DATABASE_URL"])
# Run queries in a loop to demonstrate the query capabilities.
while True:
query = input("Enter search query (or Enter to quit): ")
if query == "":
break
# Run the query function with the database connection pool and the query.
results = search(pool, query)
print("\nSearch results:")
for result in results:
score = 1.0 - result["distance"]
print(
f"[{score:.3f}] {result['product_category']} | {result['product_name']} | {result['amount']} | {result['total_value']}"
)
print(f" {result['description']}")
print("---")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
load_dotenv()
cocoindex.init()
_main()
서비스로 실행하십시오
이 예제는 Fast API를 사용하여 서비스로 실행됩니다.
요약
이 접근법은 비즈니스가 빠르고 일관된 시맨틱 + 구조화 된 검색 경험을 구축 할 수있는 강력한 새로운 가능성을 잠금 해제하여 고급 권장 사항, 지식 발견 및 하이브리드 데이터의 규모로 맥락 분석을 가능하게합니다.
단일 배치, 하나의 혈통보기 및 일관된 정신 모델을 사용하여 Cocoindex는 차세대 데이터 및 AI 전력 애플리케이션을 단순성, 엄격함 및 운영 우수성으로 구동하는 미래의 준비된 프레임 워크입니다.
우리를 지원하십시오
== 우리는 지속적으로 더 많은 예제를 추가하고 런타임을 개선하고 있습니다. ⭐ github에 Star Cocoindex를 공유하고 사랑을 나누십시오 : Heart :! 그리고 Cocoindex로 무엇을 만들고 있는지 알려주십시오. 우리는 그것들을 특징으로하고 싶습니다. ==














Post Comment